ATP molecule, The Energy Currency of Cellular Metabolism.
By Ariane Florence
ATP molecule the first law of thermodynamics states that the energy in our universe is never lost or destroyed , it is converted from one form to another . This concept can be demonstrated by analysis of how energy is derived from the environment and how this energy is converted into a form that can be used to provide the necessary living cellular processes . As animals consume this energy first through our diet ATP molecule.
The chemical energy stored in the supply of glucose is released and converted into potential energy through the catabolic pathway known as cellular respiration. This potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, ready to be used to fuel the various chemical or mechanical locomotives required for cell functions. This paper describes the processes that instigate the release of energy and how it is put to use in the body. It also seeks to explain the idea of WW" energy currency " in the cell that describes the structure and formation of the molecule responsible for providing ATP or adenosine triphosphate.
ATP molecule and sugar:
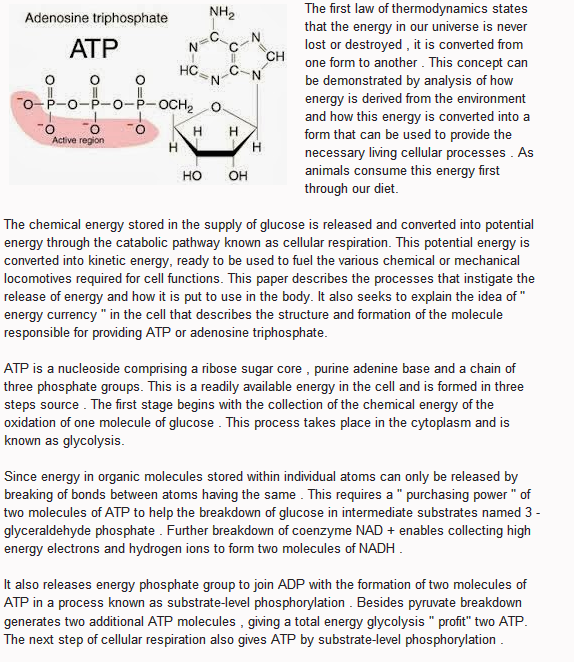
ATP is a nucleoside comprising a ribose sugar core ATP molecule, purine adenine base and a chain of three phosphate groups. This is a readily available energy in the cell and is formed in three steps source . The first stage begins with the collection of the chemical energy of the oxidation of one molecule of glucose . ATP molecule this process takes place in the cytoplasm and is known as glycol.
Since energy in organic molecules stored within individual atoms can only be released by breaking of bonds between atoms having the same . This requires a " purchasing power " of two molecules of ATP to help the breakdown of glucose in intermediate substrates named 3 - glycerol phosphate . Further breakdown of coenzyme NADA + enables collecting high energy electrons and hydrogen ions to form two molecules of NAH ATP molecule.
It also releases energy phosphate group to join ADP with the formation of two molecules of ATP in a process known as substrate-level phosphor . ATP molecule besides private breakdown generates two additional ATP molecules , giving a total energy glycol " profit" two ATP. The next step of cellular respiration also gives ATP by substrate-level phosphor .
ATP molecule this step , known as the citric acid cycle , the complete oxidation of glucose produced in the mitochondria of the cell . Private diffuses through the cell membrane and is subjected to several chemical reactions to form acetyl - Co- A, the production of carbon dioxide as a waste. NAH and FAD carry electrons also during this step as well. Two additional molecules of ATP which can be immediately used by the cell to produce energy ATP molecule.
Most ATP produced by the body is formed by the third and final stage of cellular respiration in a process called oxidative phosphor. This is known as the electron transfer step NAH and FAD giving electrons that have acquired the glycol and citric acid cycle , ATP molecule releasing energy .
ATP is processed by an enzyme called ATP syntheses using a gradient of hydrogen ions to capture the energy released by high-energy electrons . ATP molecule thus, the oxidative phosphorylation yields 34 molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose. Therefore, any chemical energy harvested from the parent molecule of glucose is present in the form of ATP , in the form of potential energy , ready to be used for cellular work .
ATP molecule potential:
ATP molecule this is the molecular basis of ATP which then allows the release of this potential energy. The degradation of ATP to ADP and subsequent regeneration is what allows each cell money to survive and carry out the work cell for a particular function. Since the three phosphate groups are negatively charged , the molecule is unstable and give up , is a terminal phosphate group by hydrolysis to form ADP ( adenosine diphosphate d ' ) and an inorganic phosphate molecule easily . This reaction is exegetic , releasing approximately -13 kcal.mol triangle. An exegetic reaction is described as when energy is released in the environment and occurs spontaneously , giving products which are less reactive potential energy ATP molecule.
Endergonic reaction requires ATP molecule an input of energy from their environment and the products have more potential energy than the reactants. It is the ability of ATP to energetic and exegetic reactions just makes that life can continue. By giving a phosphate group in the conversion of ATP to ADP exergonic , that allows others to collect and reagents to enable energy gain produced an energetic reaction . ATP molecule this process is known as the coupling of energy in the cell.
ATP molecule concept:
ATP molecule the concept of ATP as energy currency of Bourne on the idea that ATP must first be " passed " ( as two molecules of ATP steps of glycolysis ) to obtain a "gain " of 36 molecules of ATP per molecule oxidized glucose. Without continuous management and recycling of energy in our cells by ATP , we would not have the energy to make new blood , move, delete our bodies of poisons or even reproduce. The importance of ATP was highlighted in 1997 when the Nobel Prize in Chemistry was shared between Boyer, Walker & SKU , when the structure of ATP and the role of ATP syntheses ATP molecule was consolidated.


No comments:
Post a Comment